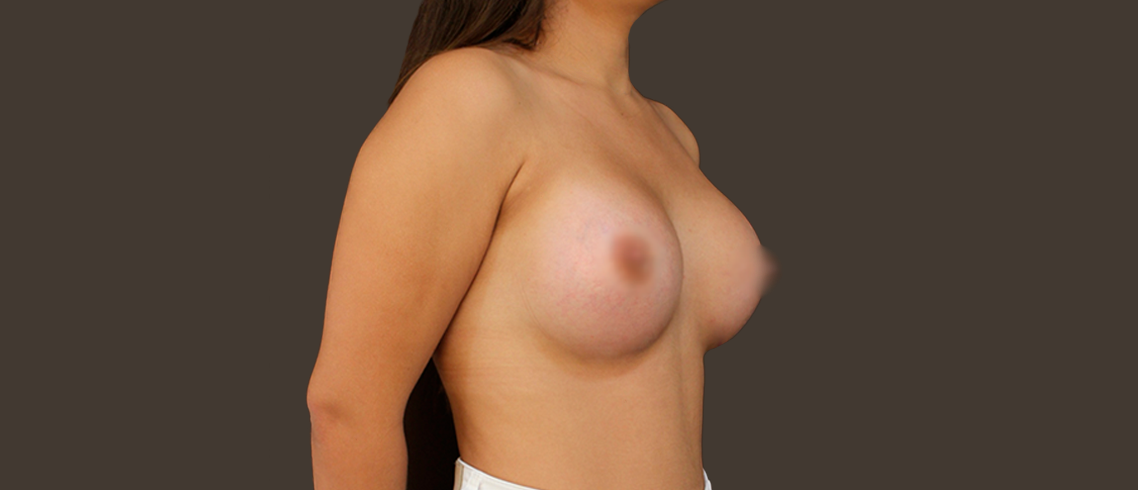
Breast augmentation, technically known as breast augmentation, is a surgical procedure to improve the size and shape of a woman's breast in the following situations: to improve the silhouette of the woman who thinks her breasts are too small to correct the Breast reduction that occurs after some pregnancies to correct a difference in size between both breasts as a reconstructive procedure after breast surgery.
FAQ
1Preparing for surgery
You will be instructed on how to prepare for surgery, including rules on food and liquid intake, tobacco or taking or suppressing medications, vitamins and iron supplements. In breast augmentation it is not necessary to transfuse blood during surgery. Also, make sure that a family member or companion can take you home when you are discharged and that, if necessary, they can help you a couple of days.
2Surgery and anesthesia
The breast augmentation is done through a small incision that is placed, depending on the patient's anatomy: around the areola or in the groove under the chest. Through this incision the breast tissue is lifted, a pocket is created and the prosthesis is placed, directly under the breast tissue or under the pectoral muscle. You can place drainage tubes that will be removed in a few days and a dressing or bandage on the breasts. The procedure lasts between 1 and 2 hours.
3After surgery
After breast surgery it is normal to find something tired a few days, but you can live almost normal life at 24-48 hours. Most discomforts are well controlled with the medication prescribed by your plastic surgeon, although the breasts may hurt a couple of weeks. The bandage or dressings will be removed in a few days, being replaced by a special bra, which you should wear as directed by your surgeon. It is normal to have a burning sensation in the nipples during the first two weeks. The stitches are removed between 7 and 14 days; The result takes time to see and it can take several weeks to observe it.
4Are there any risks?
In breast augmentation, the most frequent complication is capsular contracture, which occurs when the internal scar that forms around the implant contracts excessively, causing the breast to become harder. It can be treated in various ways, sometimes requiring the removal of said internal scar, and even replace the prosthesis.
Another complication, typical of any surgery is the hematoma that only in specific cases requires a new intervention to eliminate the accumulated blood. A small percentage of women may have an infection around the prosthesis, usually in the first weeks after surgery.
It is extraordinarily infrequent that the prostheses can break, causing the contents to come out of their capsule. When the prosthesis is filled with serum, the fluid is rapidly reabsorbed without causing any damage, reducing the volume in a few hours. If it is filled with silicone, two things can happen: if the capsule formed by the organism does not break, you will not notice any change; if it has broken, especially when it has been subjected to a lot of pressure, the silicone comes out decreasing the volume of the breast. With both types of prostheses a new intervention will be necessary to replace it.
5Results
The results after breast augmentation tend to be very pleasant for the patient. Periodic check-ups by your plastic surgeon and periodic mammograms (if appropriate for your age) will ensure that if there are any complications, it is detected on time and resolved.